Coffee Roasting Safety and Best Practices for New Operators
Coffee roasting transforms green beans into aromatic, flavorful coffee by applying controlled heat and airflow, but those same elements create safety hazards that new operators must understand and manage. This guide explains the most common hazards—fire, respiratory exposure, burns, and electrical/gas risks—why they occur in small-batch and fluid bed coffee roasting, and practical steps you can apply immediately to reduce risk. Readers will learn chaff management procedures, ventilation and monitoring strategies for VOCs and particulates, essential personal protective equipment, and a maintenance schedule tailored to minimize downtime and fire potential. The article also maps emergency preparedness actions, regulatory touchpoints like NFPA and OSHA guidance, and equipment features that materially reduce operator error. Finally, we outline how product design choices—particularly in fluid bed roasters—support safer, consistent roasting and when investing in certified equipment becomes a practical route to safer operations.
What Are the Most Common Hazards in Coffee Roasting?
Coffee roasting presents a range of hazards that stem from heat, particulates, and mechanical or electrical systems; understanding the mechanisms helps operators prioritize controls. Heat and ignition sources combined with combustible chaff create the highest fire risk, while aerosols and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from roasting produce respiratory hazards without adequate ventilation. Burns from contact with hot surfaces are common in tight workflows, and electrical or gas system faults can lead to fires or explosions if not properly installed and inspected. Slips, trips, and ergonomic strain also occur in busy micro-roasteries. Recognizing these categories allows new operators to adopt layered defenses—engineering controls, administrative rules, PPE, and emergency tools—and sets the stage for specific prevention tactics covered below.
The most critical hazards in roasting include these priority risks:
- Fire: Chaff ignition, overheated equipment, and electrical or gas faults.
- Respiratory exposure: Fine particulates and VOCs that affect air quality and worker health.
- Thermal injuries: Burns from hot surfaces, discharged beans, or process heat.
These hazard categories lead directly to actionable practices including chaff control, ventilation design, and routine inspections described in the next section.
What Fire Risks Should New Operators Know About?
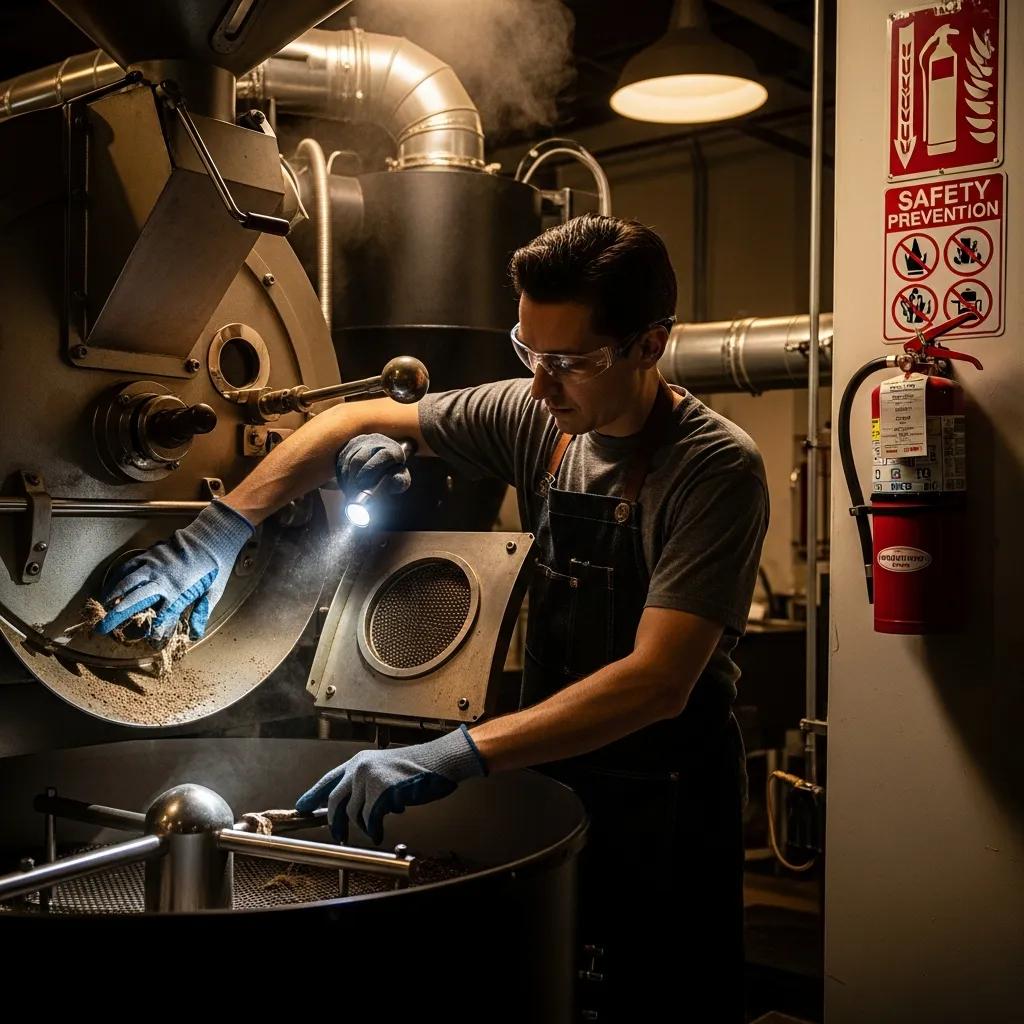

Fire risk in coffee roasting arises primarily from three mechanisms: accumulated combustible chaff contacting hot surfaces, uncontrolled temperature excursions in the roast chamber, and electrical or gas system failures that create ignition sources. Chaff is lightweight and dries quickly during roasting, and when it accumulates in collectors, ducts, or surrounding surfaces it can self-ignite at elevated temperatures or ignite from a stray spark. Electrical components that overheat or experience insulation breakdown, and poorly installed gas lines or burners, add additional ignition pathways. New operators should adopt immediate prevention actions such as regular chaff removal, strict supervision of active roasts, and clear shutdown procedures that isolate heat and fuel sources to interrupt the causal chain that leads to a fire.
Knowing common incident scenarios helps prioritize controls; for example, unattended cooling conveyors with full chaff bins are a frequent source of late-shift fires. Addressing these patterns with a combination of engineering controls (e.g., sealed chaff collectors), administrative controls (e.g., no-unattended-roast policies), and accessible firefighting equipment provides the layered safety that small roasteries need.
Let Coffee Crafters Help You Become A Coffee Roaster

What Health Hazards Affect Coffee Roasters?
Roasting releases fine particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can irritate the respiratory tract and, over long-term exposure, contribute to chronic conditions; monitoring and ventilation are essential mitigations. Acute exposures may cause coughing, eye irritation, or headaches, while repeated exposure to high particulate loads and certain VOCs has been associated with more serious respiratory outcomes; occupational guidance from agencies like OSHA underscores the importance of exposure controls. Skin and eye burns from hot surfaces or expelled beans are immediate hazards that PPE can reduce, and ergonomics matters for repetitive tasks such as bag handling and manual cleaning. New operators should pair engineered ventilation, air monitoring, and PPE selection with medical awareness and occupational hygiene practices to keep exposure within recommended thresholds.
Employing air quality monitors and reducing source emissions via process control not only improves worker health but also reduces nuisance complaints and regulatory risk, linking health controls directly to operational continuity and compliance.
How Can New Operators Manage Chaff Safely During Coffee Roasting?
Chaff management is a primary fire-prevention strategy because chaff is lightweight, combustible, and produced in large volumes during roasting; effective systems capture and isolate chaff from ignition sources. Operators should select and maintain a chaff collection approach that fits their facility—integrated chaff collectors on fluid bed roasters, external cyclone separators, or enclosed collection containers—and design workflows so that emptying and disposal occur in cool, well-ventilated areas away from heat. Regular cleaning schedules and safe tools reduce airborne dust and the chance of smoldering material accumulating in ducts or hoppers. A succinct chaff-handling program pairs equipment selection with administrative controls: defined emptying frequency, cool-down intervals before handling, and clear storage and disposal rules to eliminate pathways to ignition.
Below is a comparison of common chaff collection methods to help new operators weigh risk, maintenance, and suitability for small fluid bed setups.
This table shows that integrated collectors reduce exposure and ignition pathways compared to manual methods; choosing a system with easy access panels and predictable emptying schedules reduces operator time and risk.
What are practical cleaning and handling steps? Use the following stepwise approach to safely collect and dispose of chaff:
- Allow full cool-down: Wait until internal temperatures fall below safe handling thresholds before opening any collector or bin.
- Isolate heat & power: Engage emergency stop or isolate power before cleaning to prevent accidental startup.
- Empty into metal containers: Deposit chaff into dedicated, lidded metal bins placed away from heat sources.
- Transport and store safely: Move bins to non-combustible storage until off-site disposal or composting; avoid confined, warm areas.
Following these steps minimizes smoldering and ignition. For operators considering equipment investment, integrated collection and easy-access cleaning panels reduce both the time and risk associated with chaff handling—making it practical to Purchase Coffee Roaster models designed for straightforward chaff management.
What Are Effective Chaff Collection and Cleaning Techniques?
Effective collection relies on sealing collection paths, using appropriate materials for bins, and establishing predictable emptying intervals tied to roast volume. Integrated chaff collectors that attach directly to fluid bed roasters reduce transfer points where chaff can accumulate and smolder; external cyclone separators work well when paired with robust ducting and routine inspection. Cleaning techniques include brushing or vacuuming with HEPA-rated vacuums (used outdoors or in filtered systems), avoiding compressed air that disperses fine dust, and replacing or cleaning filters per manufacturer recommendations.
Safe disposal always requires cool-down and containment—metal bins with lids and controlled storage away from heat lessen the chance of a delayed ignition.
A consistent cleaning protocol that assigns responsibilities and documents completion further reduces risk by ensuring that chaff does not become an unattended hazard between shifts.
How Does Proper Chaff Management Prevent Fires?
Chaff acts as a ready fuel that can ignite when exposed to hot surfaces, sparks, or smoldering embers; removing and isolating chaff breaks the fuel side of the fire triangle and dramatically reduces incident probability.
Regular removal lowers the volume of combustible material, decreasing both flame intensity and potential for smoldering that can flare unexpectedly. Quantitatively, frequent emptying and sealing collection points reduce the accumulation time window during which chaff can reach ignition temperature.
Implementing a documented chaff-control program—combined with engineering choices like integrated collectors—transforms a reactive clean-up task into a proactive fire-prevention control that supports continuous, safer roasting.
What Are the Best Ventilation and Air Quality Practices for Small Batch Roasters?
Ventilation in small roasteries must balance removing heat, smoke, particulates, and VOCs while supplying adequate make-up air to maintain safe combustion and worker comfort; system design is central to respiratory risk control. Exhaust systems should create predictable airflow paths from the roast chamber to the outside, using captured hooding and ducting sized for the roaster output. Filtration options—mechanical particulate filters followed by activated carbon or catalytic VOC control where necessary—help lower emissions when full exhaust to the outdoors is constrained by local rules. Importantly, make-up air must be matched to exhaust to prevent negative pressure that can disrupt combustion appliances or draw contaminants into occupied spaces. Professional HVAC consultation is recommended for commercial setups to ensure system balance and regulatory compliance.
Good ventilation reduces airborne hazards and also preserves equipment by removing corrosive gases and heat; monitoring and periodic verification sustain performance.
How Do Ventilation Systems Improve Roastery Air Quality?
Ventilation removes the source emissions—smoke, soot, and VOCs—by capturing and transporting them away from the workspace, which reduces inhalation exposure and protects sensitive equipment. Exhaust hoods placed close to the roast discharge and properly sized ductwork minimize escape of particulates into the room, while staged filtration can trap fine particles and reduce VOC loads before any recirculation. Effective ventilation also controls ambient temperature, which improves worker comfort and reduces thermal stress that can lead to mistakes. For reliable outcomes, pair engineered systems with routine inspections and filter replacement schedules to ensure that capture performance does not degrade over time.
Investing in balanced exhaust and make-up air systems is a direct control that improves health outcomes and reduces the likelihood of nuisance complaints or regulatory violations.
What Are Recommended Air Quality Monitoring Methods?
Monitoring should combine real-time particulate counters with VOC sensors and periodic CO monitoring to provide an actionable picture of air quality and trigger mitigation when thresholds are exceeded. Place particulate sensors at breathing zone height near work areas and VOC monitors near the exhaust and in the occupied space to detect leaks or recirculation. Recommended alert thresholds should be conservative—triggering an investigation and increased ventilation when particulate or VOC readings rise above baseline roast levels. Regular log reviews, trend analysis, and calibration of sensors maintain data quality and support decisions about upgrading filtration or changing operational practices.
Deploying monitors and translating readings into immediate actions—open dampers, reduce throughput, or pause roasting—creates a responsive system that protects health and keeps operations within acceptable exposure ranges.
What Personal Protective Equipment Is Essential for Coffee Roasters?
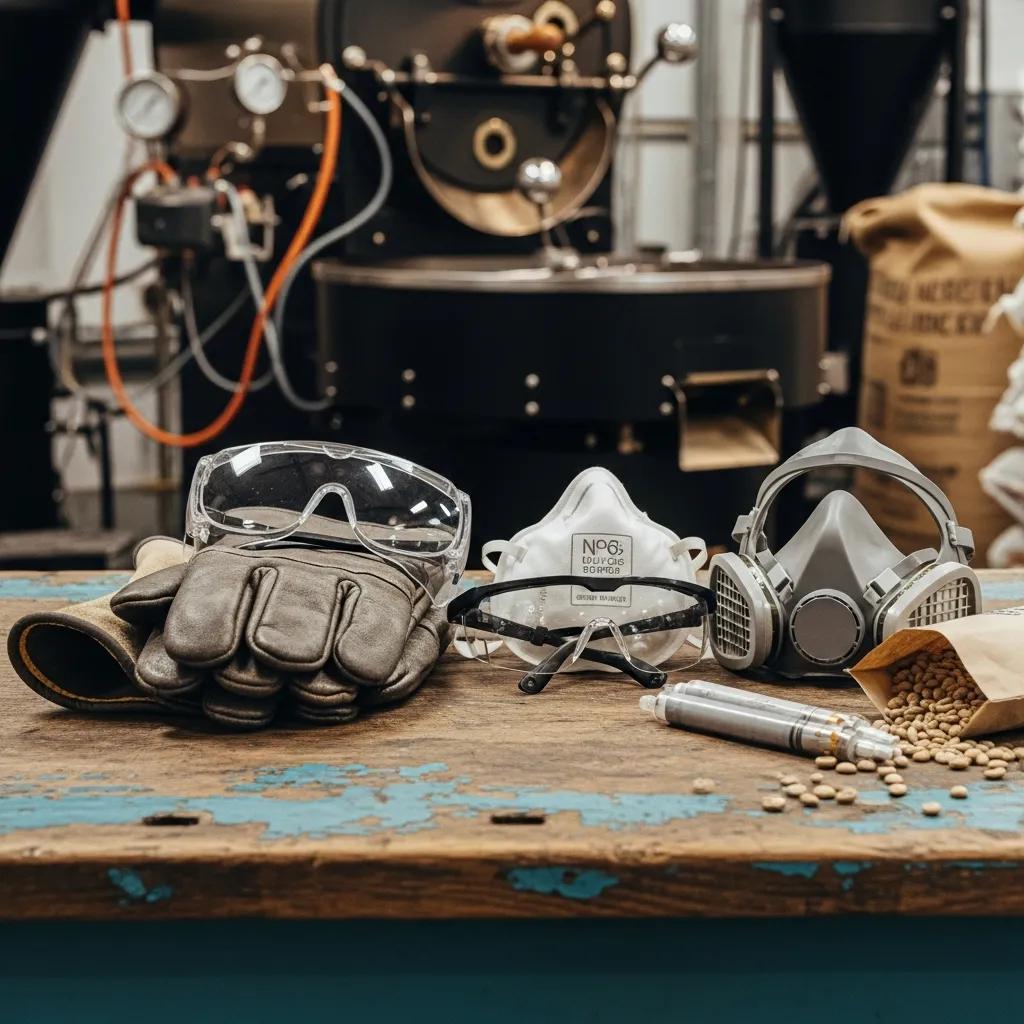

Personal protective equipment (PPE) serves as the last line of defense against burns, particulate inhalation, and eye injuries; selecting the right PPE complements engineering and administrative controls. Heat-resistant gloves protect hands during bean discharge and cleaning tasks, while eye protection prevents injury from hot bean ejecta or dust during cleaning. Respiratory protection—N95 or higher-rated respirators for particulates and elastomeric or cartridge respirators where VOCs are present—reduces inhalation risk for higher-exposure tasks or where ventilation is limited. Proper PPE selection considers task duration, exposure levels, and comfort to ensure consistent use; paired with training, PPE becomes an effective component of a broader exposure control strategy.
Operators should view PPE as part of a hierarchy: use engineering first, then administrative controls, and rely on PPE for residual risk that cannot be otherwise eliminated.
Essential PPE items for roastery operations include:
- Heat-resistant gloves: Protect hands from burns during loading, discharge, and cleaning.
- Eye protection: Safety glasses or face shields prevent particulate and hot-bean injuries.
- Respiratory protection: N95s for particulates, NIOSH-rated cartridges for VOCs when required.
Which PPE Protects Against Burns and Respiratory Hazards?
Heat-resistant gloves made from aluminized or insulated materials reduce contact burns during bean handling and equipment service, while long-sleeve, flame-resistant garments add protection for high-heat tasks. For respiratory hazards, N95 filtering facepiece respirators capture most fine particulates, and cartridge respirators with organic vapor cartridges are appropriate when VOC concentrations are significant. Eye protection with side shields and anti-fog coatings keeps visibility strong during high-temperature operations. Selecting PPE that meets recognized standards and suits task-specific exposures ensures functional protection without unduly hindering work, and helps new operators adopt consistent safe behaviors.
Pairing PPE with operational practices—like cool-down intervals and engineering capture—reduces reliance on PPE alone and creates durable protection across tasks.
How Should Operators Properly Use and Maintain PPE?
Proper PPE use starts with training on donning, doffing, and fit-checking respirators, inspecting gloves and eye protection before each use, and storing equipment in clean, dry conditions to preserve material integrity. Respirators require regular seal checks and replacement of filters or cartridges per manufacturer guidance; disposable N95s should be replaced when soiled or saturated. Heat-resistant gloves need inspection for seam integrity and should be retired when thermal barriers degrade or insulation compresses. Documenting PPE checks and training sessions helps enforce compliance and supports safety culture, while periodic reviews of PPE selection ensure continuing suitability as processes evolve.
Maintaining PPE in serviceable condition and ensuring consistent, correct use closes a final gap in the control chain and protects operators from residual risks not fully addressed by engineering.
How Should New Operators Maintain and Inspect Coffee Roasters for Safety?
A structured maintenance program prevents many hazards by ensuring systems operate within designed parameters and by catching wear or faults before they cause incidents; inspection combined with documentation is essential. Daily checks focus on visual inspections and clean-ups that remove combustible material and confirm basic controls, while weekly and monthly tasks delve into mechanical and electrical integrity, filter replacement, and verification of safety interlocks. Annual professional service should include combustion analysis, detailed electrical inspection, and verification of certification-related elements. Keeping a simple maintenance log with dates, actions, and findings supports continuity between operators and provides evidence during audits or insurance reviews.
The following maintenance schedule table maps routine tasks to recommended frequency and the safety rationale behind each action.
What Daily and Weekly Maintenance Tasks Prevent Hazards?
Daily tasks should include emptying and inspecting chaff collectors, visually checking for hot spots or discoloration on wiring, wiping down hot surfaces after cool-down, and verifying that ventilation fans are operational.
Weekly tasks expand to include tightness checks on electrical connections, inspection of duct joints and seals for chaff accumulation, filter cleaning or replacement where appropriate, and testing safety switches and alarms. Instituting a short, checklist-style routine and a log entry after each task helps maintain accountability and provides historical data to spot trends.
How Does Proper Maintenance Enhance Roaster Safety and Longevity?
Proper maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by preventing component failures and lowers the likelihood of fire or mechanical incidents by catching deterioration early; this translates into fewer emergency repairs and safer operations. Well-maintained ventilation and filtration systems maintain air quality, reducing worker exposure to particulates and VOCs, while functional safety interlocks and emergency stops prevent uncontrolled temperature excursions. From a cost perspective, proactive maintenance extends component life and avoids high-cost replacements, creating an operational ROI that justifies routine care. Simple record-keeping—dates, findings, corrective actions—also supports warranty claims and demonstrates due diligence for insurance and regulatory bodies.
For new operators, selecting equipment with easy-to-remove components and access panels reduces maintenance time and the risk associated with confined or difficult service tasks, making safe operation more achievable in busy micro-roasteries. Purchase Coffee Roaster choices that emphasize maintainability can therefore be an investment in both safety and uptime.
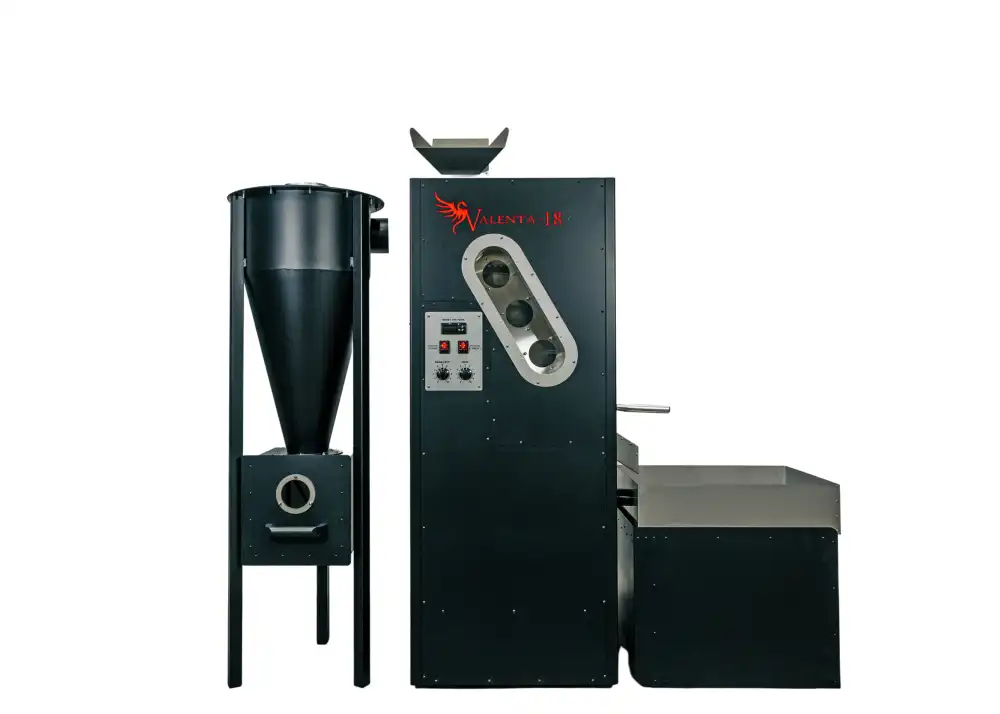
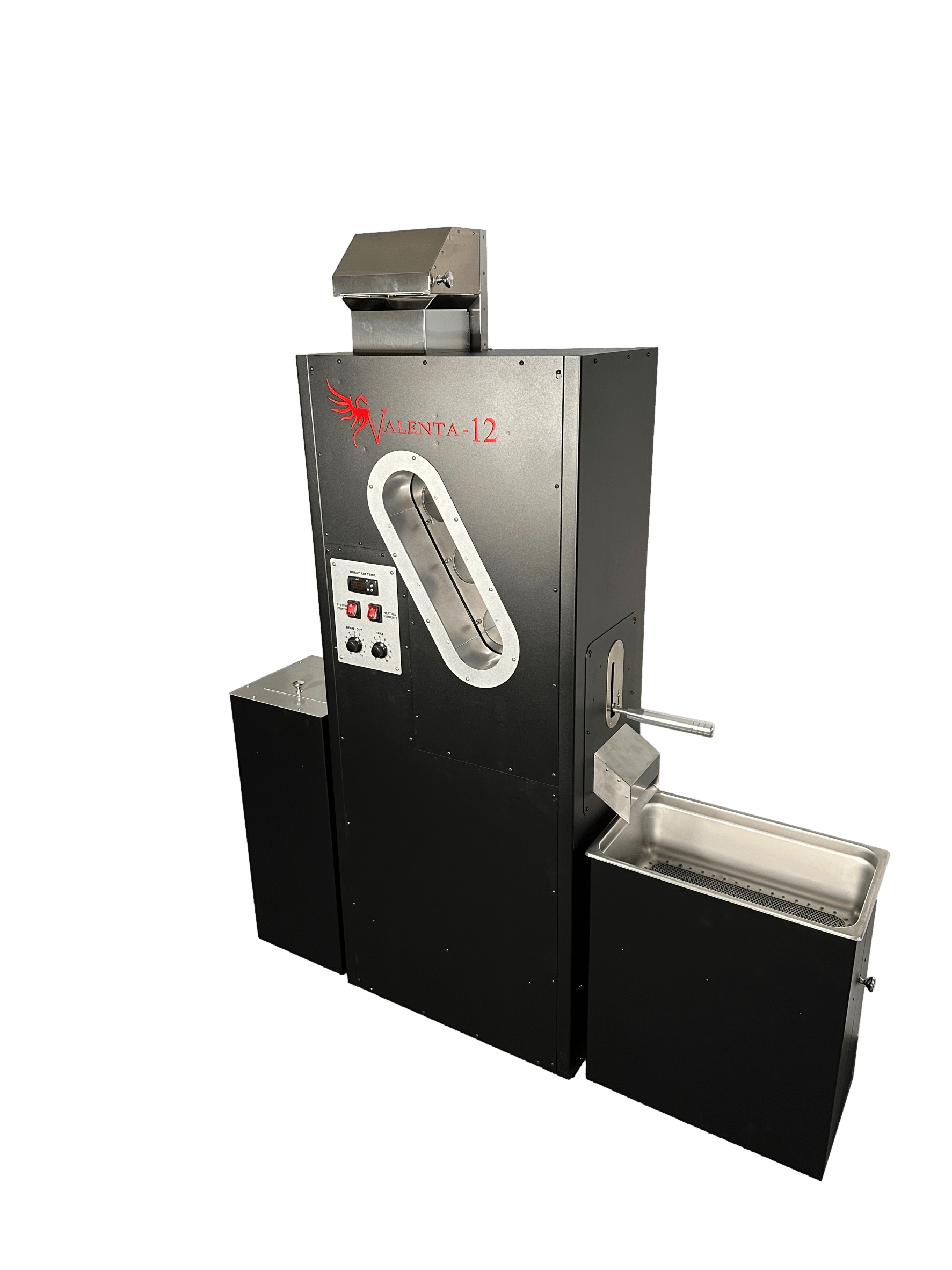
How Do Coffee Crafters’ Valenta Roasters Support Safe and Consistent Coffee Roasting?
Coffee Crafters designs and manufactures commercially certified fluid bed coffee roasters—Valenta 3, Valenta 8, Valenta 12, and Valenta 18—built for ease of installation, operation, and maintenance to support new operators seeking safer, repeatable roasting results. Key design elements include integrated chaff collectors and easy-access panels that simplify cleaning and reduce chaff accumulation risk, while commercial certification enables operation in regulated spaces where safety requirements apply. Valenta 12 and Valenta 18 models offer Hermetheus Co-Pilot software for automated temperature management, data logging, and alarms that reduce human error and help prevent overheating events. Coffee Crafters positions these roasters as affordable, American-made options with financing available, helping new operators access certified equipment that materially improves safety and consistency across roasts.
This comparison highlights how choosing a roaster with integrated chaff handling, access for maintenance, and active temperature management can reduce both the frequency and severity of safety incidents for new operators.
What Safety Features Does the Hermetheus Co-Pilot Software Provide?
Hermetheus Co-Pilot provides automated temperature regulation, customizable alarm thresholds, and continuous roast logging that together reduce the risk of overheating and unattended roast incidents by providing both active control and operator alerts. Automated control maintains setpoint stability, minimizing manual adjustments that can lead to temperature excursions, while alarm integration notifies operators of deviations early enough to intervene. Logging creates an audit trail useful for quality control and for investigating near-miss events, and historical profiles help operators standardize operations, reducing variability that can contribute to unsafe conditions. For new operators, software-assisted control reduces cognitive load and accelerates learning curves while improving reproducibility across batches.
These capabilities make automation an important safety multiplier, turning procedural vigilance into consistent, monitored outcomes.
How Does Ease of Use and Commercial Certification Improve Operator Safety?
Intuitive machine interfaces, clear access panels for cleaning, and design choices that minimize the need for confined-space maintenance reduce operator error and lower the barrier to performing routine safety tasks correctly. Commercial certification signals that equipment meets defined safety and performance standards, easing compliance with local regulatory and insurance requirements and enabling safer operation within commercial environments. Financing options make certified, safer equipment more attainable for startups, allowing operators to prioritize safety upgrades earlier in their growth trajectory.
For new operators balancing safety, cost, and scale, selecting roasters that integrate these attributes helps convert best practices into everyday realities and simplifies the path to consistent, safe production. Purchase Coffee Roaster as an option when acquiring equipment that aligns with these safety priorities.
Let Coffee Crafters Help You Become A Coffee Roaster