How to Start a Coffee Roasting Business in 2026: Complete Guide to Commercial Roasters, Profitability, and Success
Starting a coffee roasting business in 2026 means combining sensory craft with modern operations, from equipment selection to ethical sourcing and scalable distribution. This guide explains what a coffee roasting business is, why current market conditions favor specialty roasters, and how to translate roast quality into reliable margins using updated tools and controls. Many new roasters struggle to match capacity to demand, comply with evolving permits, and secure consistent green-bean supply; this article provides concrete steps to solve those problems with practical checklists, model comparisons, and planning templates. You will learn how to evaluate commercial coffee roasters, structure a business plan tied to throughput, navigate licenses and cottage food law nuances, source traceable green beans, and build marketing and automation strategies that support growth. Throughout we use terms like commercial coffee roaster, fluid bed coffee roaster, Valenta roaster, and ROI calculator to connect operational choices to profitability so you can launch a small-batch roastery with confidence in 2026.
Why Start a Coffee Roasting Business in 2026? Market Trends and Profitability Insights
Coffee roasting businesses in 2026 benefit from continued specialty coffee demand, rising direct-to-consumer channels, and technology that shortens the production learning curve. These shifts increase willingness to pay for defined roast profiles and origin stories, while automation and quality-control software reduce variability and labor costs. The result is a commercial opportunity where focused small-batch roasteries can capture local wholesale accounts and subscription revenue with healthy margins. Understanding startup cost drivers and realistic margin ranges helps founders model scenarios and identify break-even timelines before committing to equipment and lease costs.
What makes 2026 particularly attractive is the convergence of consumer preferences and accessible commercial equipment; specialty consumers increasingly favor traceability and roast freshness while roaster manufacturers offer certified, easy-to-operate fluid bed systems that lower entry barriers. This dynamic creates multiple routes to revenue — DTC subscriptions, local wholesale, and cafe partnerships — each with distinct margin profiles and scaling requirements. The following table breaks down typical startup cost categories so you can map capital needs to business strategy.
Different startup items drive one-time and recurring costs that influence early-stage profitability.
This cost breakdown highlights where capital concentrates and why equipment choice often governs viability; roaster selection determines throughput, which in turn affects required inventory, workspace, and staffing. Use these ranges to populate a conservative financial model and test scenarios with an ROI calculator before committing to a purchase.
What Are the Key Coffee Industry Trends Driving Growth in 2026?

Key growth drivers in 2026 include sustained interest in specialty coffee, increased DTC subscriptions, sustainability demand, and operational automation that improves consistency and reduces waste. Specialty coffee continues to command premium pricing when roast profiles and traceability are clear, encouraging micro-roasteries to emphasize origin storytelling. Meanwhile, many consumers now prefer subscriptions and small-batch drops that create predictable recurring revenue streams. These trends benefit roasters who can reliably reproduce profiles and document sourcing.
- 1. Specialty demand: Consumers pay premiums for single-origin traceability and consistent roast profiles.
- 2. DTC & subscriptions: Recurring shipments improve lifetime value and forecastability for small roasteries.
- 3. Sustainability and ethics: Traceable, ethically sourced lots drive buyer preference and brand differentiation.
- 4. Automation and software: Tools that log roast data and replicate profiles reduce training time and waste.
These trends imply that investment in consistent roasting processes, transparent sourcing, and subscription infrastructure yields outsized returns. The next subsection explains how those returns translate into margins and ROI expectations for small versus micro commercial operations.
Is a Coffee Roasting Business Profitable? Understanding Margins and ROI
A coffee roasting business can be profitable when gross margins, volume, and channel mix align; typical gross margin ranges run between 30% and 50% depending on pricing, packaging, and sales channels. Direct-to-consumer channels often produce higher per-bag margins due to premium pricing and subscription retention, while wholesale yields lower margins but steadier volumes. Key cost centers that compress margins include green-bean cost, labor, packaging, shipping, and equipment depreciation; controlling each element is essential to reach sustainable profitability.
- 1. Revenue drivers: Bag price, average order frequency, and number of subscribers or wholesale accounts.
- 2. Cost drivers: Green-bean cost per pound, packaging cost per bag, labor hours per kg roasted, and utility/ventilation costs.
- 3. Break-even factors: Fixed costs (facility, equipment depreciation) divided by contribution margin per bag determines monthly break-even volume.
By modeling different scenarios — micro (low-volume DTC) vs small commercial (mixed DTC + wholesale) — founders can use conservative assumptions to estimate time-to-payback. Use an ROI calculator to test pricing, throughput, and subscription retention rates so financial projections reflect realistic operational constraints.
The profitability of even small-scale coffee roasting operations can be quite significant, with potential for substantial additional income.
Profitability of Small-Scale Coffee Roasting Machines
Investment analysis reveals that using the roaster for custom work would be a profitable business with an IRR of 76% and benefit-cost ratio of 1.44. Moreover, even with the additional costs due to roasting, an average coffee farmer with one-hectare farm will get an additional income of PhP 28,240.00 from coffee roasting or an equivalent of PhP 70.6 per kilo of dried berries roasted instead of selling gre
How to Choose the Right Commercial Coffee Roaster for Your Small Batch Business

Choosing the right commercial coffee roaster means matching throughput, footprint, control, and certification to your sales plan and facility constraints. Evaluate machines by capacity (kg/hr), physical footprint, ventilation needs, ease of maintenance, and control software for profile replication; these attributes determine daily throughput, staffing, and required facility upgrades. Prioritize systems that deliver consistent roast profiles, have accessible parts and serviceability, and meet local commercial certification requirements to avoid costly retrofits and compliance delays.
An effective selection process starts by calculating target monthly roasted volume, mapping that to batch size and roast cycles per day, and then selecting a roaster with headroom for growth. Consider control software and data logging as essential features for consistency and quality assurance; roaster meronyms such as dosing blocks, conical destoners, and ventilation/filtration components materially affect throughput and cleanliness of operation. The table below compares representative fluid bed roaster models to help map throughput to business goals.
Compare Valenta fluid bed models by capacity, footprint, price range, and certification to match operational goals.
This comparison clarifies how model selection affects staffing and throughput; for example, a Valenta 12 often suits small commercial roasteries aiming to supply local wholesale accounts while maintaining DTC volume. Be rigorous about ventilation and filtration costs since these can alter total installed cost significantly.
What Are the Benefits of Fluid Bed Coffee Roasters Like the Valenta Series?
Fluid bed coffee roasters, also called air roasters, provide rapid heat transfer and often more uniform roast profiles than traditional drum roasters, which benefits small-batch operations seeking consistency and speed. The mechanism uses hot air that suspends beans, producing faster roast cycles and cleaner equipment operation, which reduces maintenance time and the need for complex drum maintenance. These characteristics make fluid bed systems particularly suitable for cafes, micro-roasteries, and small commercial sites where staff training and consistent throughput are priorities.
- 1. Consistency: Even heat distribution supports repeatable roast curves and simpler profile control.
- 2. Faster cycles: Increased throughput per hour with shorter roast times reduces labor per kg.
- 3. Cleaner operation: Less chaff accumulation and simpler maintenance lower downtime.
These operational advantages shorten the learning curve for new roasters and enable tighter quality control, which is important when scaling from sample roasts to wholesale shipments. The next subsection helps match specific Valenta models to realistic business scenarios.
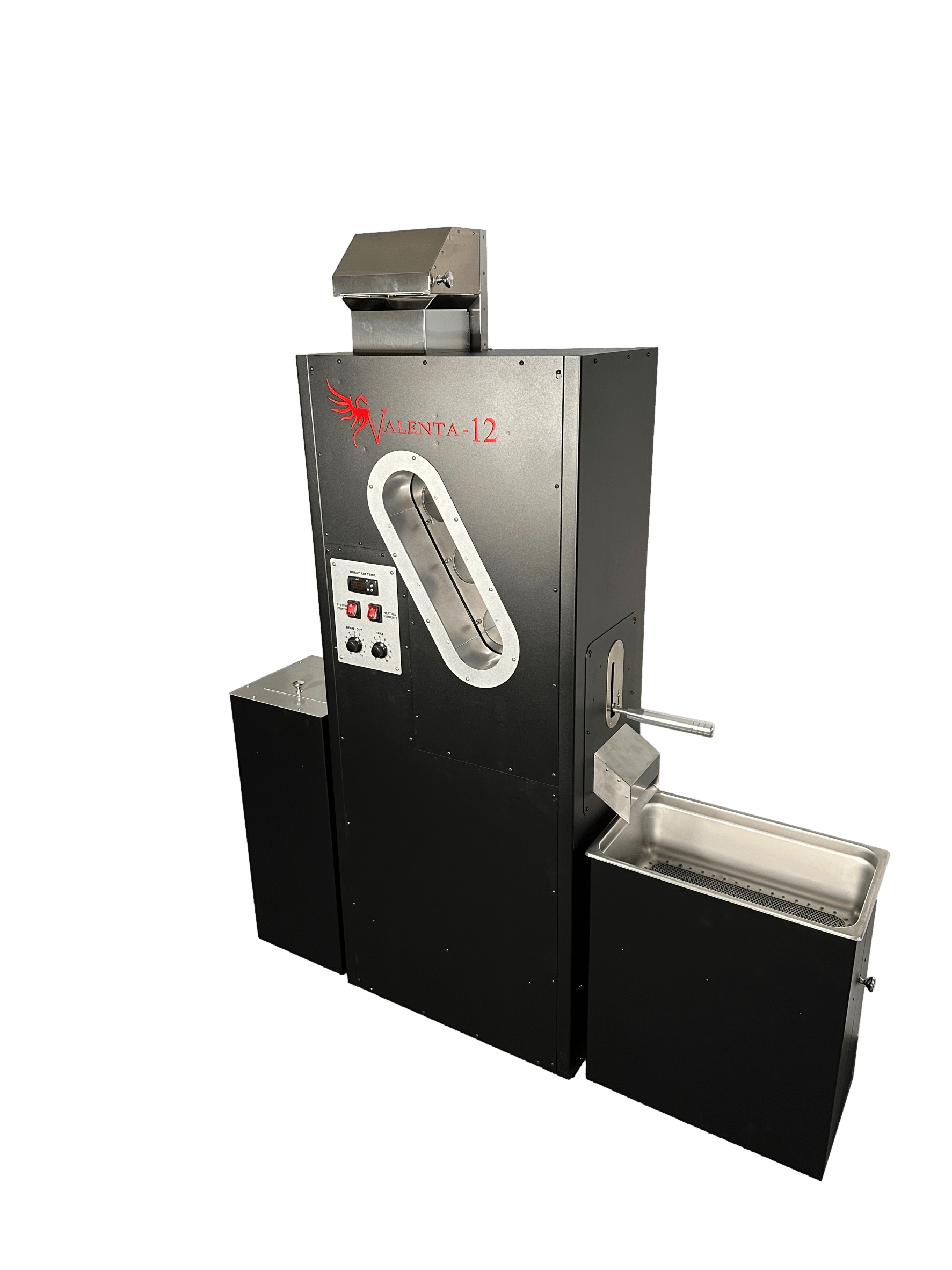
Which Valenta Roaster Model Fits Your Business Needs: Valenta 3, 8, 12, or 18?
Selecting among Valenta models depends on planned daily output, available floor space, and desired growth trajectory; smaller models suit cafe-based roasters while mid-range models often serve micro-warehouse operations. For a cafe that roasts to supply a single location and local customers, a Valenta 3 or 8 may be sufficient given limited footprint and lower daily volume. The Valenta 12 is highlighted as an affordable and productive commercial roaster for businesses launching broader DTC and wholesale channels, offering a balance of capacity and manageability.
- 1. Valenta 3: Best for tight spaces and very small-batch production.
- 2. Valenta 8: Fits cafes and small online-first operations with modest wholesale.
- 3. Valenta 12: Ideal for starting commercial volume with growth potential.
- 4. Valenta 18: Suited to higher-volume micro-roasteries supplying multiple wholesale accounts.
When mapping model to staffing, factor in roast cycle frequency, cooling capacity, and storage for green beans and packaged inventory; choosing a model with some headroom avoids immediate bottlenecks as sales grow.
After evaluating roaster specifications and business fit, consider available product support and financing options to reduce upfront barriers to entry. Coffee Crafters manufactures the Valenta series and positions these roasters as affordable, easy to install and maintain, and commercially certified. For buyers seeking a practical starting point, the Valenta lineup offers flexible model sizing and financing options, and integrates control software for precise roast control.
How to Create a Coffee Roasting Business Plan That Works in 2026
A business plan for a roastery must tie roaster capacity to sales channels, financial projections, and operational processes so assumptions are testable and adjustable. Core sections include an executive summary, market analysis, operations plan (equipment, facility, staffing), sales channels and pricing, and detailed financial projections including COGS, gross margin assumptions, and break-even analysis. Embedding equipment specs and projected roast cycles into the financial model ensures capacity constraints and capital needs are visible from day one.
- 1. Executive summary: Clear target market, value proposition, and go-to-market approach.
- 2. Operations: Roaster model, ventilation/filtration, inventory flow, and staffing plan.
- 3. Financials: Sales forecast by channel, unit economics, and break-even timeline.
Use conservative assumptions for yield loss, filler/trimming waste, and initial churn for subscription forecasts to avoid optimistic shortfalls. The next subsection explains how to use a template effectively to speed planning.
What Essential Elements Should Your Coffee Roasting Business Plan Include?
A practical plan lists specific line items and assumptions so the financial section is reproducible: projected monthly roasted kilograms, average bag price, green-bean cost per pound, packaging cost per bag, labor hours per kg, and fixed monthly overhead. Include sensitivity scenarios showing how a lower-than-expected subscription conversion or a spike in green-bean costs affects cash flow. Reference industry standard metrics from associations when estimating sales conversion and order frequency.
- 1. Sales forecast: Monthly units by channel (DTC, wholesale, cafes).
- 2. COGS detail: Green-bean cost, packaging, shipping per bag.
- 3. Operating costs: Rent, utilities, permit renewals, maintenance, depreciation.
Capturing these elements clearly allows lenders, partners, and founders to evaluate realistic capital needs and to iterate on pricing or channel strategies quickly.
How to Use a Coffee Roasting Business Plan Template for Faster Startup Success
A business plan template accelerates planning by providing structured worksheets for assumptions, roaster specs, and unit economics; start by filling the template with your chosen roaster’s capacity, projected roast cycles, and realistic yield percentages. Populate the sales forecast with conservative uptake rates for subscriptions and a phased wholesale pipeline. Run multiple scenarios through an ROI calculator to understand payback under baseline, optimistic, and conservative cases.
- 1. Customize capacity inputs: Enter roaster kg/hr and expected daily cycles to compute monthly throughput.
- 2. Validate pricing: Test bag price points and subscription discounts against margin targets.
- 3. Stress test: Simulate green-bean price spikes and slower subscription growth to assess runway.
Coffee Crafters provides a downloadable business plan template and an ROI calculator as practical tools to speed this process and to align equipment choices with financial projections, enabling founders to make informed purchasing decisions more quickly.
Let Coffee Crafters Help You Become A Coffee Roaster

What Licenses and Permits Do You Need to Start a Coffee Roasting Business?
Permits and licensing depend on scale and sales channels, but common requirements include food facility registration, health department approval, business license, and local fire or air-quality permits where applicable. Cottage food laws may apply for very small producers in some jurisdictions, but roasted coffee often falls into gray areas; many states treat roasted coffee differently from other cottage food products. Verifying local health department interpretations is essential to avoid retroactive compliance costs.
Regulatory items interact with equipment and facility decisions: ventilation and filtration upgrades often trigger air-quality or fire permits, and zoning rules determine whether customer-facing roasting in a commercial area is permissible. The table below summarizes typical permits and applicability to help prioritize regulatory research and budgeting.
Because regulations vary, consult local authorities early in site selection and include estimated permit costs in your budget model to avoid surprises that delay opening.
How Do Cottage Food Laws Affect Small Coffee Roasters in the USA?
Cottage food laws are state-level frameworks that allow limited production of certain foods from a home kitchen for direct sale, but their applicability to roasted coffee is inconsistent across states. Some jurisdictions explicitly exempt roasted coffee while others require formal food facility registration when selling beyond direct face-to-face transactions or when volume thresholds are exceeded. The determining factors are typically sales channel (DTC online vs in-person), annual revenue, and whether the product is considered non-potentially hazardous.
- 1. Yes/No framework: If your state treats roasted coffee as a non-cottage product, you must register as a commercial food facility.
- 2. Triggers for commercial registration: Selling wholesale, shipping across state lines, or reaching defined revenue thresholds.
- 3. Practical step: Contact local health department to confirm classification before expanding sales channels.
If cottage rules do permit home roasting, maintain meticulous records and label products per state requirements; when in doubt, plan for commercial registration to avoid enforcement risks.
What Other State and Local Permits Are Required for Commercial Roasting?
Beyond cottage law classification, typical permits include air quality approvals for ventilation systems, fire inspections, building occupancy, and local business licenses; some jurisdictions require plan review for commercial-grade roasting equipment. Zoning approval is essential if you plan to operate in mixed-use areas, and health department inspections focus on labeling, traceability, and sanitation procedures. Including permit timelines in your project schedule prevents delays in equipment installation and production start.
- 1. Air quality / ventilation: May require engineering plans and permits for exhaust and filtration.
- 2. Fire & building safety: Inspections and possible requirements for suppression systems.
- 3. Local business & zoning: Confirm manufacturing use is allowed in the selected site.
Budget both the permit fees and potential facility modifications into your startup cost table to ensure capital adequacy and realistic opening dates.
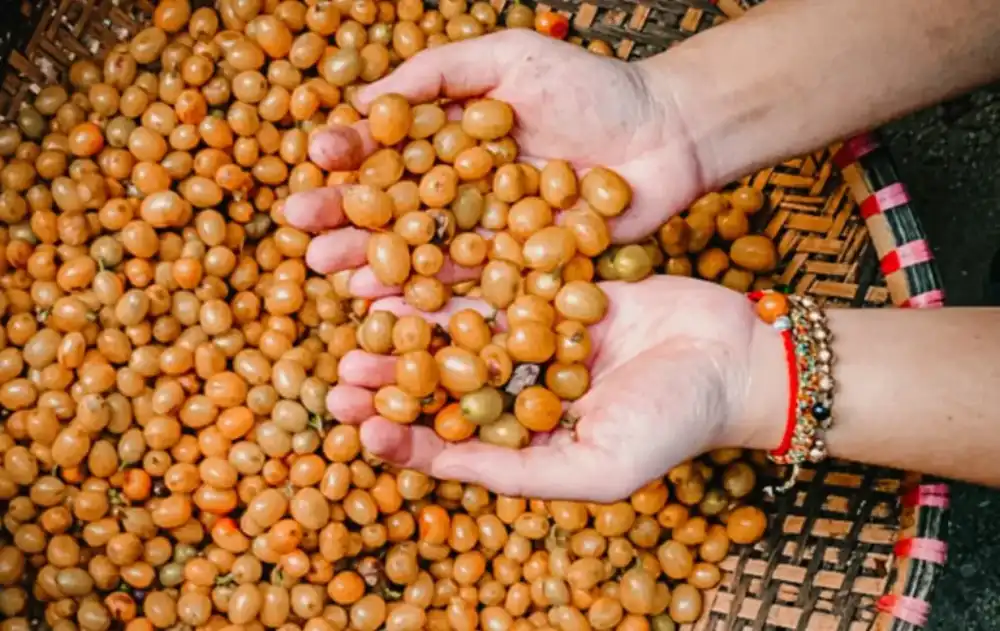
How to Source Quality Green Coffee Beans for Your Roastery in 2026
Sourcing green coffee begins with defining the flavor profile and quality goals for your roastery, then establishing relationships with importers or partners who provide traceability, sample roasts, and reliable logistics. Evaluate origin, grade, processing method, and lot traceability through sample orders and cupping before committing to full lots. Start with small pilot lots, roast-off samples, and standardized cupping protocols to determine how a bean performs across your roast profiles.
- 1. Origin selection: Choose origins that align with your flavor identity and customer expectations.
- 2. Sample and roast-off: Always request samples and perform controlled roast-offs to assess behavior.
- 3. Logistics: Factor in lead times, storage, and import costs when planning reorder cadence.
Relationship-building with reputable suppliers mitigates risk and can secure better lot access; the following subsection explains how partner channels can simplify sourcing while remaining vendor-neutral first.
Let Coffee Crafters Help You Become A Coffee Roaster
Why Choose Ethically Sourced Green Beans from Wholesale Origin?
Ethical sourcing improves traceability, consistency, and consumer trust while supporting sustainable farm-level practices, and partnering with reputable importers speeds procurement and quality control. Working through a partner that emphasizes traceability reduces time spent investigating farms and lots, and often provides sample availability and consistent grading. Ethical sourcing may come at a premium but can be justified by higher retail pricing and stronger brand positioning in specialty markets.
- 1. Traceability: Verified origin stories enable better storytelling and quality assurance.
- 2. Consistency: Partner importers often offer QC and access to repeatable lots.
- 3. Brand value: Ethical sourcing resonates with specialty consumers and supports premium pricing.
As an actionable option for roasters seeking simplified procurement, Coffee Crafters partners with Wholesale Origin to provide green beans and streamline sourcing; use partner channels when you need dependable lots and documentation that support quality claims.
What Are the Best Practices for Selecting Green Coffee Beans for Small Batch Roasting?
Adopt a disciplined sampling and cupping workflow: request green samples, perform roast-offs with identical profiles, cup blind, and log results using consistent scoring metrics. Control storage conditions to preserve lot integrity—store green coffee in cool, stable humidity environments and rotate inventory based on first-in, first-out principles. When scaling from samples to full lots, increase lot size gradually and maintain active communication with suppliers about potential variability.
- 1. Sampling protocol: Roast identical sample batches and cup using a standard form.
- 2. Storage: Maintain stable temperature and humidity, and monitor for pest control.
- 3. Scaling cadence: Move from sample to micro-lot to full-lot buys as confidence grows.
These practices reduce the likelihood of surprises at scale and help maintain consistent roast profiles that customers expect from specialty roasters.
How to Market and Scale Your Coffee Roasting Business Successfully
Marketing and scaling a roastery requires a balanced mix of DTC subscriptions, local wholesale partnerships, and digital presence that leverages origin storytelling and roast consistency. Prioritize a small set of channels at launch—local cafes, farmers’ markets, and targeted online subscriptions—while building processes that support fulfillment, inventory management, and quality control. As volume grows, invest in automation, staff training, and systems that reduce variability and operational friction.
- 1. Channel mix: Start local, prioritize high-margin DTC, and expand wholesale selectively.
- 2. Brand differentiation: Use origin stories, roast transparency, and sustainability claims to stand out.
- 3. Fulfillment: Ensure packaging and logistics scale with subscription growth to maintain delivery promises.
A coherent marketing rhythm combined with reliable roast reproduction creates positive word-of-mouth and repeat purchases, which are crucial for sustainable scaling.
What Are Effective Marketing Strategies for Small Coffee Roasters?
Effective strategies center on sampling, local partnerships, curated drops, and subscription offers that encourage trial and retention. Launch with in-person tastings at local cafés or markets to build a base, then convert interest to subscriptions through limited small-batch releases and onboarding incentives. Use clear origin and roast-profile storytelling to educate customers and justify premium pricing, and measure acquisition costs against average lifetime value to refine channel focus.
- 1. Local partnerships: Collaborate with cafes and food vendors for exposure and trial.
- 2. Sampling programs: Offer small roast samplers to remove purchase friction.
- 3. Subscriptions & drops: Promote recurring revenue through curated monthly or seasonal releases.
Implement tracking for acquisition channels and customer cohorts so you can prioritize tactics that deliver sustainable ROI and reduce churn over time.
How Can Automation and Software Like Hermetheus Co-Pilot Improve Roasting Consistency and Efficiency?
Automation and roast-control software improve consistency by recording roast curves, enabling profile replication, and reducing dependence on operator memory, which lowers waste and shortens training time for staff. Systems that automate logging and profile control help scale quality across shifts and locations, and they provide data that informs yield optimization and defect reduction. Reduced variability translates into lower rework, fewer customer complaints, and improved margin stability as volume increases.
- 1. Consistency: Automated profile replay reduces roast-to-roast variability.
- 2. Efficiency: Data-driven adjustments cut waste and optimize energy use.
- 3. Training: New operators achieve consistent results faster with profile automation.
Hermetheus Co-Pilot is an example of such software that integrates with modern roasters to log profiles and automate roast replication, delivering practical gains in consistency and reduced operational waste for roasteries that prioritize scale and quality.
Let Coffee Crafters Help You Become A Coffee Roaster









